What is Colonoscopy?
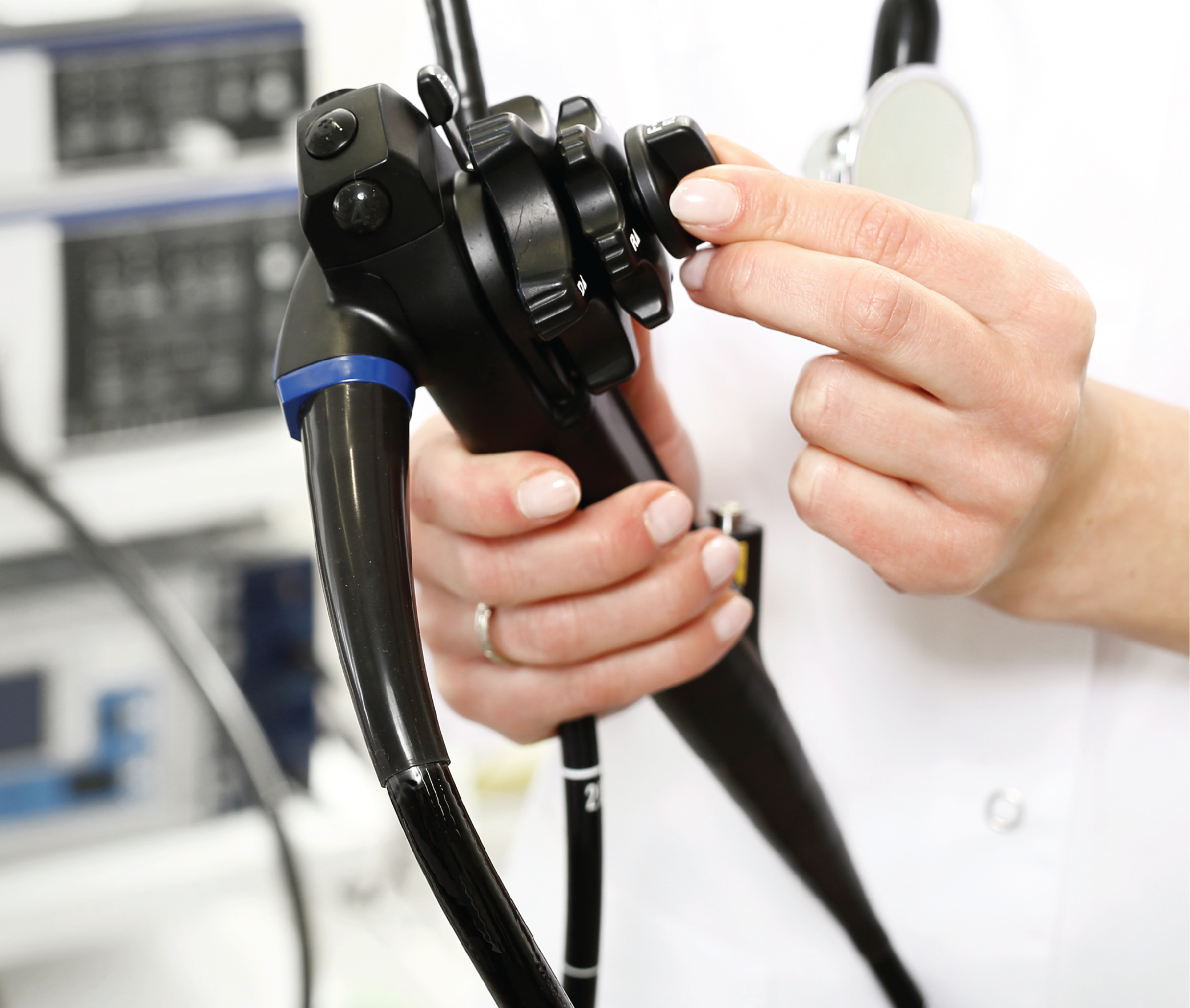
A colonoscopy lets your doctor examine the large intestines (colon) to find out the cause of bowel-related issues. Colonoscopes have several hollow channels for suction, air & water delivery and biopsy taking. The examination uses a flexible fibreoptic camera inserted through the anal canal into the large intestine.
Why it is Done?
- To help diagnose lower gastrointestinal tract bleeding or blood in stool
- To discover the cause of acute and chronic diarrhoea
- To screen for colorectal polyps and cancers
Is There Any Risk?
Colonoscopy is a safe procedure. There is a minimal risk of bleeding or perforation (tear in the bowel). Fewer than 0.001% of people experience bleeding or perforation.
What You Can Expect
Before the procedure
|
|
A low-fibre diet is prescribed before the exam. Fasting is required for atleast 8 hours before the exam. |
|
|
Laxatives are given to cleanse the bowel. |
|
|
Inform your doctor if you are on any anti-coagulants, anti-platelets or blood thinners. |
After the procedure
|
|
It takes about an hour to recover from the sedation. It is recommended for you to have someone take you home because it can take up to a day for the full effects of the sedative to wean off.Do not drive, make important decisions or go back to work for the rest of the day. |
|
|
Bloating and passing wind are common occurrences after the procedure. Walking may help to relieve discomfort. |
|
|
If a biopsy or polypectomy was performed, you may notice a small amount of blood in the first bowel movement after the exam. This is usually not a cause for alarm. |

Discharge Instructions Post-scope
- You are encouraged to start your diet by sipping water or cool liquids and having soft food. You can resume your normal diet once you feel better.
- In some instance, you may not have fully recovered from the sedation.
- You are NOT encouraged to drive, operate heavy machinery, drink alcohol, conduct business or sign legal documents.
- You are advised to go home and REST. If you have problems, go straight to the hospital for further assessment.
Complications
- Bleeding (usually after a biopsy or removal of a polyp)
- Perforation or puncturing in the digestive tract
- Infections
- Depressed breathing from sedation